
Knowing what transmission the car has is one of the most important factors when considering which car to buy. From Manuals, Automatics, CVTs, and DCTs, the list goes on. A car’s transmission or gearbox is what transfers power from the engine to your car’s wheels through a system of gears and gear trains.

There are many types of car transmissions. It’s important to know that each type works differently and each has its own pros and cons.
So to help you decide which might suit you and your preference best, let’s go over 5 of the most common transmissions you’ll find when shopping for a car.

Manual Transmission (MT)
Table of Contents
The manual transmission, otherwise known as the “stick shift”, is one of the most basic transmissions out there. Well, except for the driver that is, since, with a manual, the driver will need to shift gears constantly using the car’s clutch pedal and the gear stick.

How does it work?
- The manual transmission sees a set of gears with a flywheel and pressure plate connected to the car’s engine with the clutch right in between them together with the input and output shaft.
- When you press on the clutch pedal, this releases the pressure plate which in turn disengages the clutch from the engine, letting you change gears.
Advantages
- Being the simplest form of transmission, this would lead to easier and less expensive repairs compared to other types. Not to mention that here in the Philippines at least, manual transmission cars can go for much less than their automatic counterparts.
- MTs are also better for off-roading since they can provide a high torque load. They also offer (relatively) better performance and fuel efficiency compared to automatic or CVT. The catch is that the driver has to learn the skill of driving a manual well in order to get the most out of it.
- Car enthusiasts and driving purists have also loved the manual transmission as it gives the driver a sense of control when driving and getting the timing of shifting gears is just a feeling like no other.
Disadvantages
- The only downside really for manual transmissions is its high learning curve and the effort the driver puts in when driving one.
Automatic Transmission (AT)
The automatic transmission is the most common type that you can find today and it is much simpler to operate than a manual.
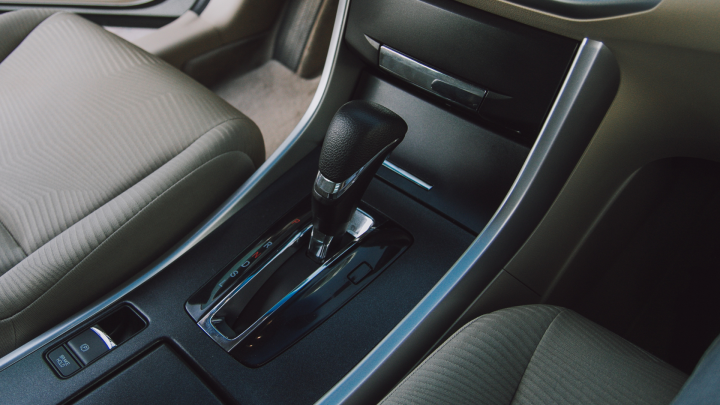

How does it work?
- What sets an automatic transmission from a manual is the fact that it doesn’t use clutches but rather a Torque Converter to shift gears. It transmits the engine’s rotational energy and eliminates the need to manually shift gears and the car’s onboard computer help to do so.
Advantages
- This makes automatic transmissions much easier to drive making learning how to actually drive a car much easier for the majority of us.
- Although manuals are thought to be more fuel efficient and better performing than automatics, most modern automatics are more advanced than the automatics of yesteryear. The fuel economy of automatic vehicles has already improved as we speak.
Disadvantages
- The downside is that behind the simplicity of its gear shift with P-R-N-D-L, it actually is more complex mechanically compared to a manual. This increases the chances of something going wrong and being more pricey to repair. Oh, and vehicles with automatic variants will also cost a little bit more than their manual counterpart.
- While not exactly a disadvantage, automatics with more gears get a little bit better fuel mileage. The more gears an AT has, the more effectively and efficiently utilize the engine’s power for efficiency and performance. It’s not an exact science, but more gears may be better.
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
Besides manual or automatic transmissions, another type that’s caught on in recent years is the DCT or dual-clutch transmission.
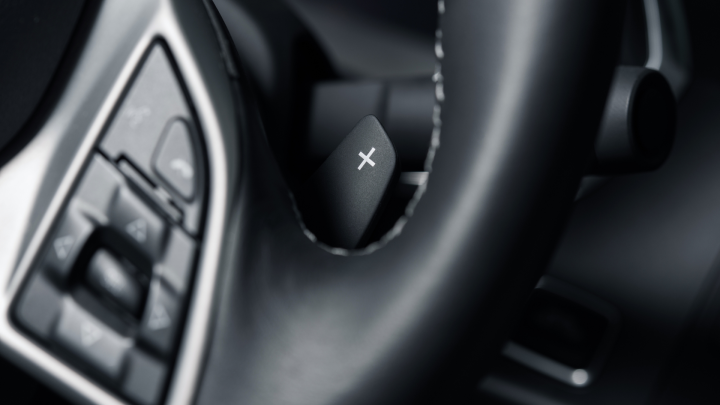

How does it work?
- A DCT will feature two separate clutches for its odd (1,3,5, and reverse) and even gears (2,4, and 6), this results in much faster gear shifts.
- A computer on-board also controls the clutch engagement and gear shifts which makes it somewhat a crossover between a manual and automatic.
- DCTs either operated generally much like an automatic car but can also be operated manually with paddle shifters.
Advantages
- You’ll often see DCTs on high-performance cars due to their quick gear changes that are smooth and accurate. DCTs also offer better fuel economy than traditional automatic transmissions.
Disadvantages
- However, that also comes at the cost of mechanical complexity which leads to them being rather expensive and costly to repair if an issue occurs.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
Nowadays, you’ll also see what they call a CVT or a continuously variable transmission. You’ll commonly see these, but are not limited to, on most small vehicles.
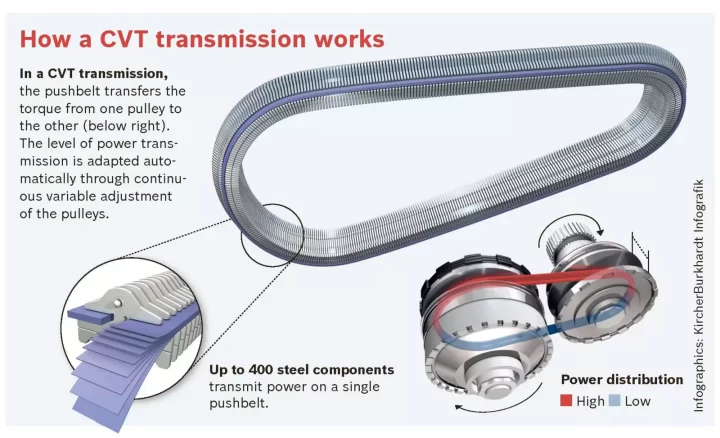
How does it work?
- A CVT is similar to an automatic transmission but with the exception of having no gears at all. Instead, it has a continuously variable drive ratio using a system of belts, pulleys, and sensors which allows it to have infinite gear ratios that help maintain a steady acceleration with no gear changes.
- The car’s computer adjusts the pulleys to create optimal ratios in whatever driving situation.
Advantages
- The biggest advantage of a CVT is its fuel economy due to it being able to keep the engine in its optimal power range.
- However, they are less prone to issues and are a little bit more affordable and cheaper to repair when compared to an automatic.
Disadvantages
- Depending on the person, a CVT’s smooth acceleration can be either a pro or a con. Among car enthusiasts, having no gearshifts when driving but rather just simply accelerating smoothly may leave some drivers feeling less enthusiastic. However, for most of us who just care about getting from point A to B, CVTs offer the smoothest of rides.
- Another disadvantage of a car with a CVT is that you wouldn’t really want one when driving off-road due to its limited torque-handling ability. You’ll also see that CVTs may require more maintenance with repairs being quite costly due to the wear and tear of the belts.
Automated Manual Transmission (AMT)
An AMT or automated manual transmission is similar to a traditional manual vehicle with a clutch but with the exception of having no clutch pedal. Instead, the clutch’s action and shifting itself are done by using a system of electronics and hydraulics with sensors and actuators.
This allows drivers to either have fully automatic gear shifts or manual shifts through paddle shifts or a gear shift with a – or + sign to shift gears up or down.
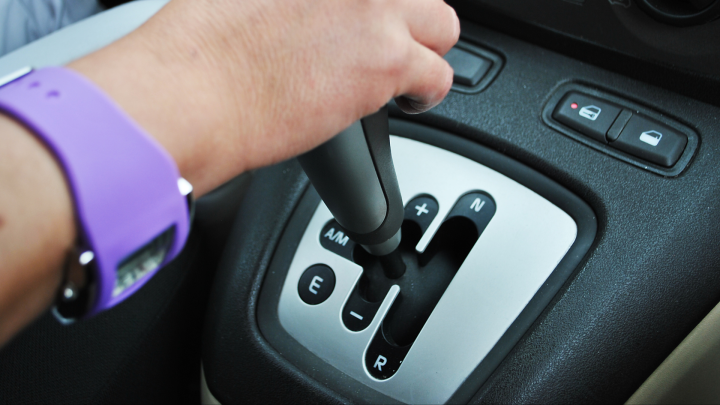

How does it work?
- Instead of having a gear stick and a clutch pedal, an AMT has a hydraulic actuator system inside the engine which operates both. The actuators are linked to the car’s computer unit which controls the gears and clutch with a pre-programmed gear shift pattern.
Advantages
- The main upside of using an AMT over a traditional manual is that you won’t be needing to operate the clutch anymore, making it much easier to drive.
- But you also get the added benefit of having more control similar to a traditional manual. AMTs are also generally considered to be more fuel efficient than automatic transmissions.
Disadvantages
- Sounds like the best of both worlds right? But AMTS are also known to have gear shifts that are sometimes not as consistent and could lead to the feeling of jerkiness.
–
And there we have it, the 5 most common transmissions available in the Philippine automotive market today. Tell us what your transmission of choice is and why in the comments section. It’ll be very interesting to see who are new- and old-school among our readers.





